Web Client VS RPC Client
If you're unsure which client to use for interacting with the Nimiq blockchain, this page offers a comparison between the Nimiq Web Client and the RPC so you can choose the tool that best fits your needs and expertise.
TL;DR
The Nimiq Web Client establishes direct connections with other peers in the network, making it a part of the blockchain network. In contrast, the RPC follows a client-server model, where clients connect to a single server that interacts with multiple peers on the network.
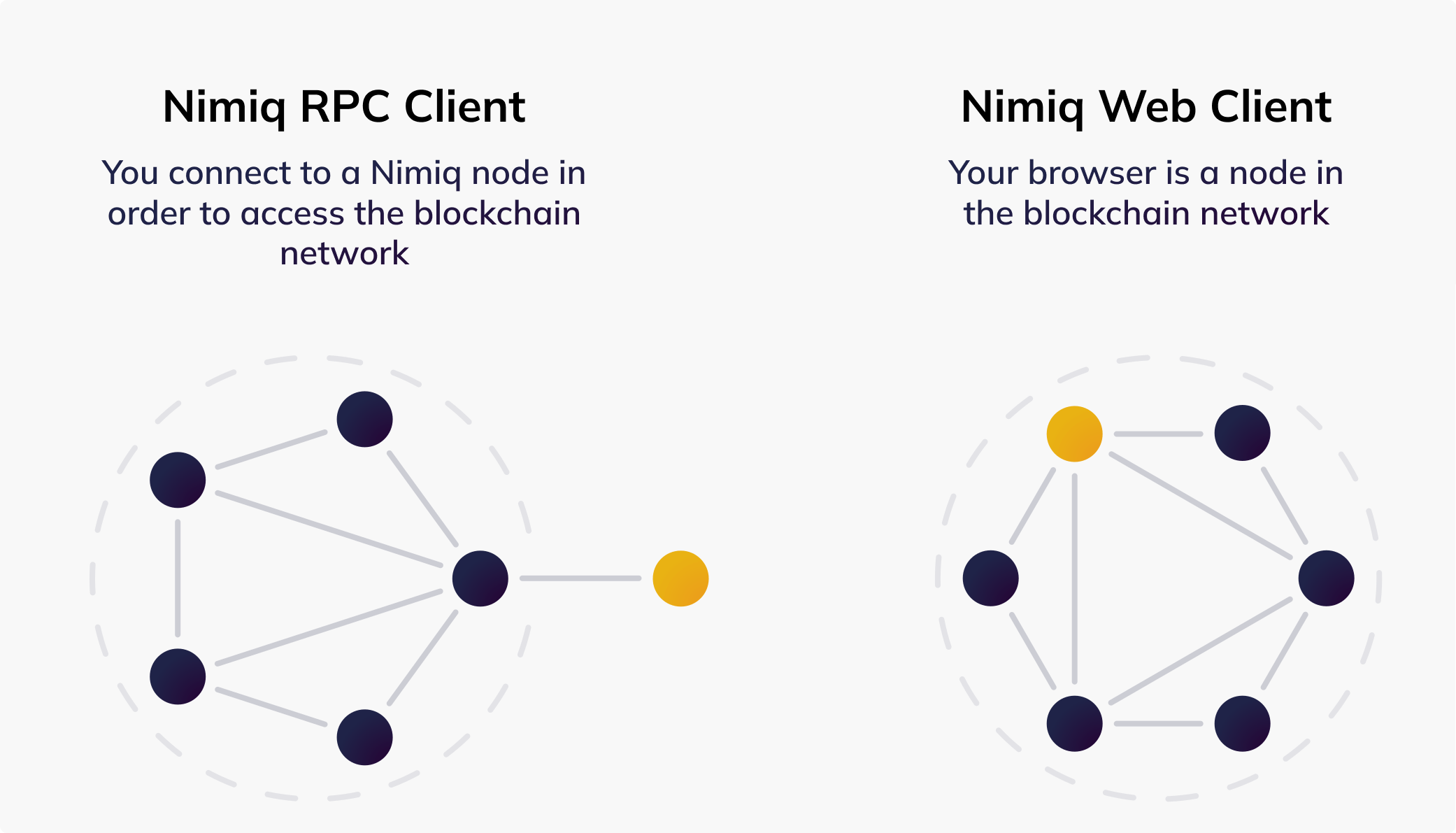
Nimiq Web Client
The Nimiq Web Client is a JavaScript library that enables direct participation in the Nimiq PoS ecosystem directly from your web browser. This client is compiled from Rust to WebAssembly and offers a lightweight solution for users who want to interact with the Nimiq blockchain.
The Web Client provides a user-friendly interface for building consensus with other nodes, creating wallets, sending transactions, and interacting with the blockchain with simple operations. It simplifies user interaction and offers easy integration.
Users can access the Web Client on mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, providing flexibility and convenience for managing their Nimiq wallets and transactions on the go. The Web Client is designed to be compatible with major web browsers, including Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Microsoft Edge, ensuring a consistent user experience across different platforms.
Nimiq RPC
The Nimiq RPC provides developers access to a node that is part of the Nimiq blockchain and establishes a connection between a client and a single server, which then interacts with multiple peers on the network.
The RPC offers more elaborate functionalities, such as retrieving information about the blockchain state, submitting transactions, managing accounts, and configuring node settings. It is particularly valuable for developers and nodes who require advanced control and automation of blockchain operations.
The RPC supports interaction with nodes and allows users to call its endpoints using JavaScript, shell scripting languages, or any language or software capable of sending requests according to the JSON-RPC specification. Comprehensive API documentation is available for the RPC, detailing the methods, parameters, and endpoints supported by the interface, facilitating seamless integration and development.
How to know which one to use?
| Aspect | Web Client | RPC Client |
|---|---|---|
| Nimiq Use | Nimiq Pay App | TrustWallet |
| Accessibility | Requires familiarity with JavaScript and similar frameworks like NodeJS; can be run in a browser | Requires adherence to the JSON-RPC specification |
| Functionality | Basic blockchain tasks | Gives detailed control over blockchain functions |
| User Base | Easy for beginners | For developers, experienced users, validators |
When interacting with the Nimiq blockchain, users have the option to choose between the Web Client and the RPC, each offering distinct advantages based on their needs and expertise. Let’s take a look at what you can do with both.
Web Client
For users seeking a straightforward and user-friendly way to interact with the blockchain, the Nimiq Web Client is the ideal choice. With its intuitive interface, users can perform basic operations such as creating wallets, sending transactions, and checking balances within their browsers. The Web Client simplifies blockchain interactions, making it accessible to users of all skill levels. Some of the operations supported by the Web Client include:
- Create new wallet addresses
- Send transactions to other addresses
- View transaction history
- Check account balances
RPC
For developers, tech-savvies, and validators looking for more advanced control over blockchain operations, the Nimiq RPC provides extensive capabilities for accessing their nodes. Through established methods and endpoints, users can perform a wide range of operations, including:
- Create new accounts
- Create special transactions, such as deactivating validators or redeeming early HTLCs
- List all available accounts and their balances
- Subscribe to updates for head block hashes and consensus establishment
- Retrieve ZKP state information