View change
The Albatross consensus algorithm was built to adapt its behavior in case some validators act maliciously.
The view change protocol is inspired by the PBFT algorithm, tolerating up to one-third of malicious validators. When a validator fails to produce a block because it went offline, or even if it purposely wants to delay the block, other validators request a view change on the current validator.
View change protocol
A view change is a change of the view slot, and it occurs every time a validator does not produce the new block in a preset time Δ. When a validator delays producing a block, the rest of the validators from the validators slot list will request a view change by sending a view change message. This protocol only runs in micro blocks, since macro blocks have another protocol to deal with delays.
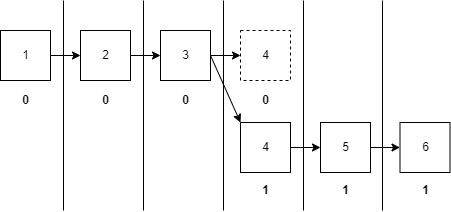
Figure 1 - the block number is inside of the block and the view number is under the block.
To choose a new validator, a random seed from the previous block and the new view number are used to select the new validator to produce the micro block. This new view slot has Δ time to produce the block.
Using figure 1 as a reference, after the validator finishes producing block 3 and the slot for block 4 is randomly chosen, the new validator has Δ time to produce block 4. The validator will run an algorithm following these steps:
- Wait for a new block; if the block is produced, the algorithm terminates, and a new block is added to the blockchain.
- If the time elapses, request a view change by sending a view change message to the network. Wait for either a new block or 2𝑓+1 view change messages.
- If the block is received from the delayed validator, it is added to the blockchain. If 2𝑓+1 view change messages are received, a new validator is selected and the algorithm restarts in step 1.
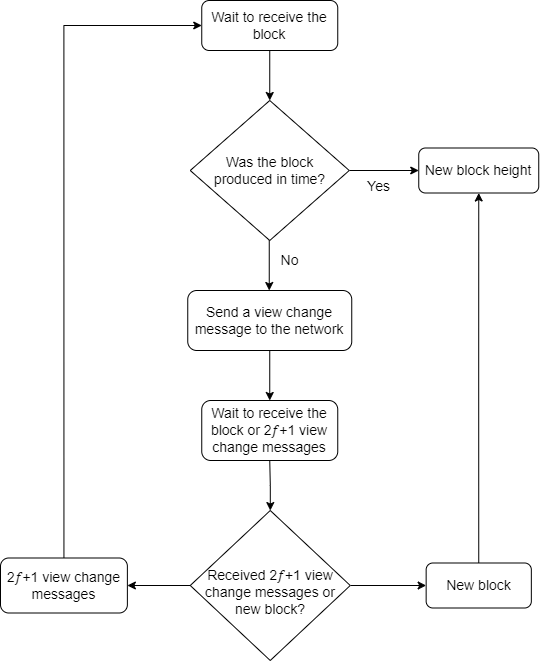
Figure 2
It is necessary to consider these aspects:
- A view change can be requested after the preset time for producing the new block has elapsed.
- Given 3𝑓+1 validators, considering 𝑓 to be malicious, it is required 2𝑓+1 view change messages to proceed with the protocol, otherwise, the validator must wait for a new block or 2𝑓+1 view change messages.
- When a view change happens, the view number increases by one, therefore, the chain with priority is the one with the highest view number.
- If a validator receives 2𝑓+1 view change messages, it won’t accept a block from the delayed validator. The outcome of receiving 2𝑓+1 view change messages is always a view change in the validator.
- If the delayed validator produces several blocks, they will be reverted once 2𝑓 + 1 view change messages are received.
- The view change message is signed and sent by a validator slot. A validator that holds 𝑥 validator slots, signs 𝑥 messages.
View change message
A view change message is sent when an elected validator requests a view change. It sends a message to the rest of the elected validators containing these fields below:
Block number u32: The number of the micro block that is being produced (block number 4 in figure 1)
View number u32: The view number of the micro block that should be in production (block 4, view number 1 in figure 1)
Previous random Seed VrfEntropy: The random seed of the previous micro block (block number 3 in figure 1)
The view change message is signed and sent by each validator slot.
View change proof
When a view change is requested and the validators run the view change algorithm, the block must include a view change proof, proving that a view change occurred in that block. This proof is added to the micro block justification and is an optional field, since a view change may not happen in a block. The proof consists of the aggregated BLS signature of the slots who have signed the view change message.